这考医学院的物理题,我看了头都炸了
娃回家准备开始复习MCAT,拿半套diagnostic exam测试一下
物理我懂的,拿他一道题看看,头一下就炸了。这是物理吗?common core害死猫 
Oral drug delivery systems are limited by the short gastrointestinal transit time, leading to low bioavailability. Drug delivery systems able to retain the dosage form in the stomach are needed. Research into floating drug delivery systems (FDDS) may satisfy this need.
FDDS can be approached by either effervescent or non-effervescent techniques. Ideal effervescent techniques achieve floating duration times > 16 hours in the stomach. Effervescent FDDS incorporate gas-generating agents, which provide buoyancy. Newer research focuses on non-effervescent systems, where the swelling of polymers joined to the drug entraps air within the polymeric matrix, providing buoyancy to the dosage form.
A study was performed on the antidiabetic sulfonylurea glipizide. The drug and one of three polymers were mixed in a mortar according to the ratios described in Table 1. A drop of water was added, and the mixture was kneaded until a homogenous paste was obtained. The mixture was then placed in an oven at 50°C for 30 min to remove water. The compound was then compressed into tablets which served as the basis for drug release and buoyancy measurements.
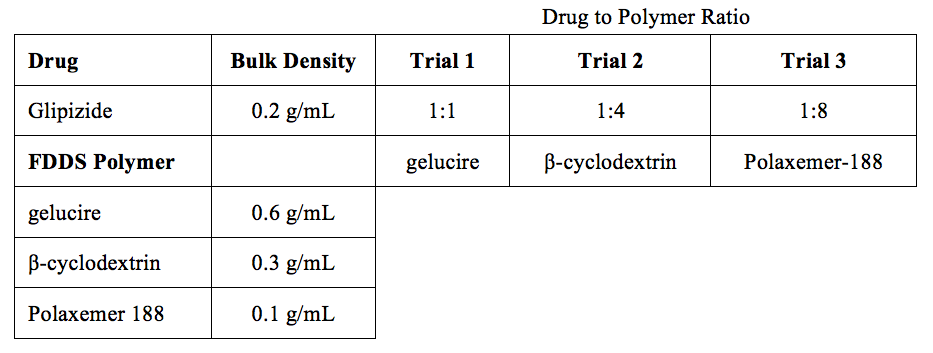
Table 1 The density of glipizide and the three polymers and the drug to polymer ratio in each trial
To test in vitro drug release of solid dispersions, the tablets were placed into dissolution vessels containing 900 mL of 0.1 M HCl. Dissolution studies were carried out for one hour, with samples withdrawn at predetermined intervals. Drug concentrations were assayed using HPLC methods. The dissolution experiments were carried out in triplicate, and the results are shown in Figure 1. In vitro buoyancy was also tested. Tablets were placed in a vessel containing 500 mL of 0.1 M HCl. The time taken for the tablet to rise to the surface of the dissolution media (floating lag time) and total duration that the tablet remained on the surface (total floating time) were recorded.

Figure 1 Drug release as a function of time and pill composition
The Ksp for glipizide-cyclodextrin in a chyme solution at 37ºC was determined to be 5.8 x 10-4. Increased solubility of drug dispersions may be achieved by wetting via hydrophilic polymers, or by polymer size reduction.
(Note: all pills for the above trials have the same volume.)
Which of the following correctly lists the floating lag times for the three trials in increasing order? (note: assume that the mixing of the drug and polymer does not change the density of either component)
Trial 1 < Trial 2 < Trial 3
Trial 2 < Trial 1 < Trial 3
Trial 3 < Trial 2 < Trial 1
The passage defines lag time as the time taken for the tablet to rise to the surface of the dissolution media. Object flotation is determined only by density – a less dense object will rise quickly in a fluid and will then float with more of its volume above the fluid surface. A more dense object will rise more slowly and will float with more of its volume submerged. (An even more dense object may sink.)
At this point, you may guess that the pill with the least dense polymer (trial 3) will rise the most rapidly, giving it the smallest lag time. That would lead you to choice C and you could move on. However, if you wish to do the calculations for density, they are listed below. Note that we are told that all pills have the same volume, so to determine the density of a particular pill, we must simply find the weighted average of the density of its components:
Trial 1 is a 1:1 ratio of glipizide (ρ = 0.2) and gelucire (ρ = 0.6), so the density of the pill is:
(1/2)(0.2) + (1/2)(0.6) = 0.4
Trial 2 is a 1:4 ratio of glipizide (ρ = 0.2) and β-cyclodextrin (ρ = 0.3), so the density of the pill is:
(1/5)(0.2) + (4/5)(0.3) = 0.28
Trial 3 is a 1:8 ratio of glipizide (ρ = 0.2) and polaxemer-188 (ρ = 0.1), so the density of the pill is:
(1/9)(0.2) + (8/9)(0.1) = 0.11
Trial 2 < Trial 3 < Trial 1
1.35%
22.6% of students answered this question correctly
