下面这篇文章讲解了利率,房价的关系。房子是防通货膨胀的。但也不是总是通胀高,房价就高。但利率越高,房价的增长大多数情况下,越低。
Correlation of mortgage rates with real housing prices: How increasing inflation could affect housing prices。

Correlation of mortgage rates with real housing prices: How increasing inflation could affect housing prices
I was talking with a friend who was telling me that it was the absolute perfect time to buy a house because housing prices have tumbled and interest rates are low.
I asked him, “What happens to housing prices if there is inflation and rates go up?”
“Housing prices should go up with inflation as they do for all goods. Housing is a natural hedge for inflation”
Did my friend have a point? Yes and no.
Yes, he was right that in a high inflationary environment, housing prices should rise with all other assets. Rents will go up, as will the price of all the inputs into housing such as lumber and labor costs.
Obviously, housing prices will go up to reflect this reality.
But no, when inflation and thus nominal interest rates increase, housing prices tumble. When rates fall, housing prices tend to increase.
Relationship between mortgage rates and housing prices
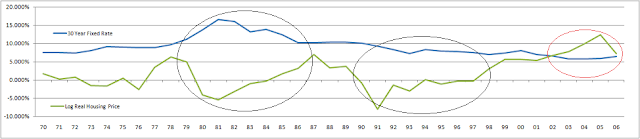
You can see an obvious correlation by looking at the following graph of interest rates and the log of real housing. The two black circles are areas where the correlation is obvious. The third red circle is an area where the correlation seems less relevant.
The simplest explanation for this correlation comes down to payment. Most people have to finance their homes. As such, they make housing decision based upon monthly payment, i.e. what they can afford. If a borrower with 2,000.00 available per month for a mortgage, they could afford to finance about $372,500 over 30 years with a 5% rate. If that rate were to increase to 10%, the amount they could afford to finance would drop by almost 40% to $273,000.
From 1982 to 2003, there was a long term trend of dropping mortgage rates. During this same term, we had a general improvement in the change in housing prices. The exception was 1990 to 1991 where there is a period of negative changes to housing prices that aren’t explained by the mortgage rates. Also, from 2003 to 2006, mortgage rates stabilized, but housing increased dramatically. New products such became popular such as subprime mortgages and payment option arms that allowed lower payments so people could afford more housing and thus drive up the price even while mortgage rates were stable